Pandas and Their Habitat: A Closer Look
Key Takeaways
- Pandas primarily inhabit mountainous regions in China, predominantly in Sichuan, Shaanxi, and Gansu provinces.
- Their natural habitat consists mainly of bamboo forests, which are vital for their diet.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to protect their dwindling habitats from human encroachment and climate change.
- Understanding pandas' behaviors and habitat requirements can help improve conservation strategies.
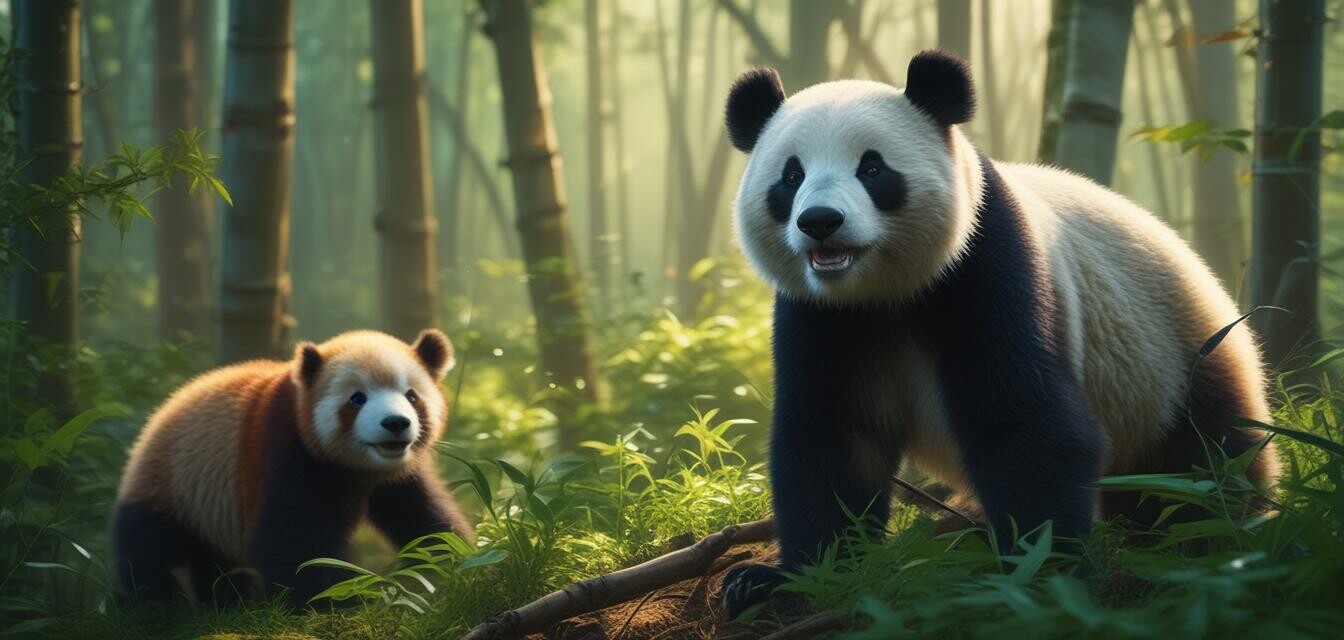
Pandas are not only one of the most beloved animals in the world, but they also play a crucial role in their ecosystems. In this article, we’ll dive deeper into the natural habitats of pandas, what they require to thrive, and the conservation challenges they face in today’s world.
Where do pandas live?
Pandas primarily reside in the mountainous regions of China. This restricted habitat is mainly located in three key provinces: Sichuan, Shaanxi, and Gansu. The topography of these regions provides the specific conditions needed for the survival of the giant panda.
Geographical locations
| Province | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Sichuan | Home to the largest population of pandas, featuring extensive bamboo forests. |
| Shaanxi | Offers a mix of bamboo growth and mountainous terrain. |
| Gansu | Less populated but essential for panda conservation efforts. |
Panda habitats: The bamboo connection
Bamboo makes up about 99% of a giant panda's diet. Therefore, its availability is crucial for their survival. Pandas require large areas of bamboo forests to access sufficient food, which leads them to roam extensively within their habitats.
Types of bamboo
Not all bamboo species are suitable for pandas; they prefer certain varieties based on their nutritional content. Some of the most common types include:
- Phyllostachys edulis (Moso bamboo)
- Fargesia spp. (Clumping bamboo)
- Amorphophallus konjac (Elephant yam, sometimes eaten by pandas)
Conservation challenges
Despite being adorable, pandas are facing serious threats to their habitats. Below are some of the most pressing challenges:
Pros of habitat conservation
- Preservation of biodiversity in the ecosystem.
- Enhances tourism and local economies.
- Improves scientific understanding of wildlife behavior and ecology.
Cons of habitat loss
- Decreased panda populations as their food source diminishes.
- Increased human-wildlife conflict as pandas encroach on human territories.
- Long-term impacts on plant and animal diversity in the ecosystem.
Efforts in panda conservation
Conservation efforts play an essential role in protecting the giant panda and their habitats. Let's take a look at some of the key strategies employed:
- Protected areas: Establishing reserves to safeguard bamboo forests.
- Bamboo planting programs: Restoring deforested areas with suitable bamboo species.
- Education campaigns: Raising awareness about pandas and promoting conservation.
Panda reserves in China
Some of the most notable panda reserves include:
| Reserve Name | Location | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Wolong National Nature Reserve | Sichuan | One of the largest panda reserves in China. |
| Chengdu Research Base of Giant Panda Breeding | Sichuan | Focuses on breeding and conservation efforts. |
| Bifengxia Panda Base | Sichuan | Addresses ecological restoration and habitat management. |
Conclusion
Pandas are not just cute animals; they are a vital part of their natural habitat. Understanding their shelter needs, dietary requirements, and the challenges they face is crucial for their survival. By working towards effective conservation strategies, we can help ensure that these magnificent creatures thrive in their natural environments. For more insights about these adorable animals, visit our blog on Red Panda Facts and Panda and Red Panda Buying Guides.